| Forest Road Deactivation Practices | |
| in the Pacific Northwest | |
| 17 - Cross-Ditching Practices | Helpful Hints, Backup Cross-Ditches |
Always excavate the cross-ditch from outlet to inlet. The cross-ditch inlet must be deeper than the base of the road ditch. Larger flows and steeper grades will require deeper cross-ditches. Armour outlet areas if erosion is expected. The size and placement of armour depends on anticipated flows and the risk to downstream values. Consider other means of erosion protection if rock is not readily available. Frequent cross-ditches can also be used to disperse hillslope drainage where unstable slopes exist below the road. Consciously choose safe locations for cross-ditches - never "just kick the water off the road". If access is to be maintained, carefully grade the approaches to allow for vehicle traffic. Remember a good rule of thumb: a cross-ditch should be at least five times wider as it is deep!
Always install the berm on the downgrade side of a cross-ditch, regardless of the direction of deactivation activities. To maintain or re-establish natural drainage patterns, cross-ditches should always be installed working downhill from the highest point.
Figure 16: Position of Berm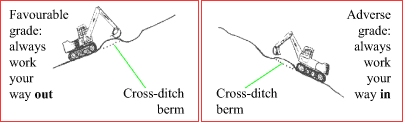
If you anticipate erosion of the base of the cross-ditch, use armour to protect the base. In situations where frequent high flows are expected, but frequent vehicle access is required, consider the design and installation of fords and armoured swales.

Backup cross-ditches are installed directly downgrade of the culvert location, unless otherwise instructed. Check with your supervisor in your access management plan if vehicle access must be maintained. Backup crossditches should be equal in size to the cross-sectional area at the highwater mark of the channel, and similar in design and shape to a regular crossditch. The height of ditch blocks at culverts and cross-ditches is important, and varies with the intended level of deactivation.
Install sediment control if water at the cross-ditch is flowing directly into fish habitat, or into a watercourse which is connected to fish habitat or a domestic water intake. Consider that you have the option to dewater channels to minimize the introduction of sediment into watercourses. Note the placement of armouring at the outlet of the above cross-ditch.
| 17 - Cross-Ditching Practices |
| Next |
||
|
|
|
©1999 - 2002 Flip Productions Limited Used with permission by CulvertBC |